Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Overview
- 3 Tables
- 3.1 Table creation
- 3.2 Columns – Creating and Adding to Tables
- 3.3 Deleting/Removing Columns
- 3.4 Modifying Column Properties
- 3.5 Clearing Column Collection
- 3.6 Cloning a Table
- 3.7 Rows – creating and adding to a table
- 3.8 Modifying data within an existing table row
- 3.9 Fill Table using LoadDataRow() method
- 3.10 Retrieving Table Content
- 3.11 Row Versions and Accepting/Rejecting Changes
- 3.11.1 Methods and Enumerations
- 3.11.2 Sample 1 – Row States
- 3.11.3 Sample 2 – Initial Loading of Table
- 3.11.4 Sample 3 – DataRow AcceptChanges
- 3.11.5 Sample 4 – Table AcceptChanges
- 3.11.6 Sample 5 – DataRow BeginEdit
- 3.11.7 Sample 6 – DataRow CancelEdit
- 3.11.8 Sample 7 – DataRow BeginEdit – Example
- 3.11.9 Sample 8 – DataRow Change values – Example
- 3.11.10 Sample 9 – DataRow EndEdit – Modified Rows
- 3.11.11 Sample 10 – DataRow AcceptChanges of Modified Rows
- 3.11.12 Sample 11 – DataRow RejectChanges
- 3.11.13 Sample 12 – LoadDataRow without table having primary key
- 3.11.14 Sample 13 – LoadDataRow with table having primary key
- 3.11.15 Sample Code for Obtaining Version and State Information
- 3.12 Handling DataTable Errors
- 3.13 DataTable Events
- 4 Data Sets
- 4.1 DataSet Methods
- 4.2 DataSet Properties
- 4.3 Loading A DataSet
- 4.3.1 From a Table
- 4.3.2 From a Database
- 4.3.2.1 Method 1 – sqlDataAdapter
- 4.3.2.2 Method 2 – sqlDataReader
- 4.4 Linked Tables
- 4.5 Linked tables in a dataset
- 4.5.1 Filling
- 4.5.2 Removing
- 4.6 XML Export and Import DataSet Data
- 4.6.1 WriteXml
- 4.6.2 ReadXml
- 4.7 Handling DataSet Errors
- 4.8 Updating Database with DataSet/DataTable changes
- 5 Data Grid
- 5.1 Methods and Properties
- 5.2 Assigning Data Sources
- 5.3 Formatting
- 5.3.1 DataGridTableStyle – WinForms
- 5.3.2 Change only one table’s DataGridTableStyles
- 5.3.3 Change a single column in a Table’s DataGridTableStyle
- 5.3.3.1 Method 1 – for-loop through collection
- 5.3.3.2 Method 2 – Direct access using column string name
- 5.3.4 Create a DataGridTableStyle for Tables Based upon its Data
- 5.3.5 Defining DataGridTableStyles through Visual Studio .NET IDE
- 5.4 Navigation
- 5.4.1 CurrencyManager
- 5.4.2 CurrentCell
- 5.4.3 Selecting Rows
- 5.4.4 Expand and Collapse linked tables
- 5.5 Copy DataGrid to the Clipboard
- 5.5.1 Copy selected table in DataGrid to clipboard
- 5.5.2 Copy all tables in DataGrid to clipboard
- 5.5.3 Format table data into a string
- 5.6 Exporting to a Tabbed delimited Text File
- 5.7 Cloning Table contained in a DataGrid
- 5.8 Comparison of WinForms & WebForms
- 5.8.1 WinForms
- 5.8.2 WebForms
- 5.8.2.1 Edit a row
- 5.8.2.2 Cancel editing a row
- 5.8.2.3 Entering a new row
- 5.8.2.4 Updating a row
- 5.8.2.5 Setting Cell Style values
- 6 References
1 Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide a practical guide to using Microsoft’s .NET DataTables, DataSetsand DataGrid. Most articles illustrate how to use the DataGrid when directly bound to tables within a database and even though this is an excellent way to use the DataGrid, it is also able to display and manage programmatically created and linked tables and datasets composed of these tables without being bound to a database. Microsoft’s implementation has provided a rich syntax for populating and accessing rows and their cells within tables, for managing collections of tables, columns, rows and table styles and for managing inserts, updates, deletes and events. Microsoft’s Visual Studio .NET development environment provides detailed explanations and code examples for the classes, which is excellent for obtaining a quick reference to a method or property, but not for understanding how they all fit together and are used in applications.
This article will present different ways to create and manage bound and unbound tables and datasets and to bind them to DataGrids for use by WebForms and WinForms. The different behaviors of the DataGrid depending upon whether it is in a WebForm or a WinForm will be presented. In addition, copying DataGrid content to the clipboard, importing and exporting in XML and printing will be presented. Techniques for linking DataGridcontent to features within graphics objects to provide an interactive UI will be discussed in the last section.
The intent of this article is not to be a complete reference for all methods and members of the classes used for building Tables, Datasets and DataGrids, but to illustrate systematically how to build and manage them using their essential methods and properties. The article will also show equivalent ways for working with these entities to illustrate programming flexibility options. Once they are built the tables can be added to a database and/or the content easily extracted for updating existing database tables.
The structure and features of a table created using the DataTable class is at the heart of using the DataGrid; therefore, it will be presented first. Next the DataSet that manages collections of independent and linked tables will be presented followed by the DataGrid that displays and provides an interactive UI for its Tables and Datasets. All example code will be written in C# and the periodic table with its elements and isotopes will be used as a model and source of data.
2 Overview
Figure 1 is a summary view of the essential relationships between the DataGrid, DataGridTableStyles,DataSets and DataTables and their various methods and properties. This article will delve into the details of each of these components describing how to create them, to fill them with data and how they work together and thereby provide a clearer understanding of this relationship diagram.
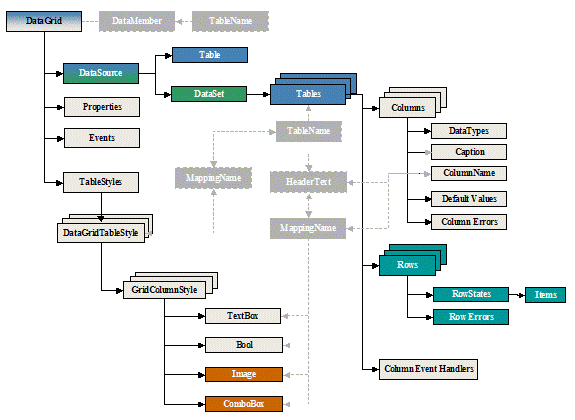 Figure 1 DataGrid, DataSet and DataTable relationship diagram
Figure 1 DataGrid, DataSet and DataTable relationship diagram
Next…
License
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL)
